Understanding Legionnaires’ Disease in Lincoln, NH
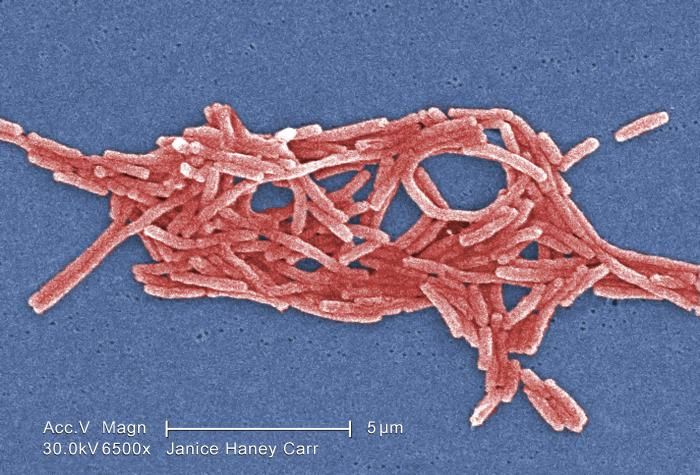
Legionnaires’ disease is a serious type of pneumonia caused by bacteria called Legionella. It is not spread from person to person, but rather through inhaling contaminated water droplets. The disease can be fatal, especially for individuals with weakened immune systems.
Prevalence of Legionnaires’ Disease in New Hampshire and Lincoln
Legionnaires’ disease is a relatively uncommon illness, but it can occur anywhere in the United States, including New Hampshire. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that there are approximately 8,000 to 18,000 cases of Legionnaires’ disease reported each year in the United States. However, the actual number of cases is likely higher, as many cases go undiagnosed or unreported.
There are limited publicly available data on the prevalence of Legionnaires’ disease in specific areas of New Hampshire, including Lincoln. This is because reporting requirements for Legionnaires’ disease vary by state, and data collection and reporting practices may not be consistent.
Potential Risk Factors in Lincoln, NH
Several factors can increase the risk of Legionnaires’ disease outbreaks in any community, including Lincoln. These factors include:
- Presence of contaminated water sources: Legionella bacteria can thrive in water systems, especially those with warm water temperatures and stagnant water. In Lincoln, this could include hotels, motels, and other accommodations with large water systems, as well as public water systems, and even private wells.
- Presence of older infrastructure: Older water systems may have more opportunities for Legionella bacteria to grow, as they may have more pipes and fittings that can harbor bacteria. This is especially relevant in Lincoln, a town with a significant number of older buildings and infrastructure.
- Seasonal factors: Legionnaires’ disease outbreaks tend to occur more frequently in the summer months, when water temperatures are warmer and people are more likely to use water-based recreational activities.
- Large gatherings: Large events, such as conferences or festivals, can increase the risk of Legionnaires’ disease outbreaks, as they can bring together large numbers of people who may be exposed to contaminated water sources. Lincoln is a popular tourist destination and hosts various events throughout the year.
- Presence of vulnerable populations: Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as the elderly, people with chronic illnesses, and those who are immunocompromised, are at increased risk of developing Legionnaires’ disease.
Impact of Legionnaires’ Disease on Lincoln, NH

The potential impact of Legionnaires’ disease outbreaks on the local community of Lincoln, NH, is multifaceted, encompassing both health concerns and economic implications. While the community has experienced outbreaks in the past, its resilience and proactive measures have contributed to its ongoing recovery and preparedness.
Health Concerns
Legionnaires’ disease is a serious bacterial pneumonia that can be fatal, especially for individuals with underlying health conditions. Outbreaks in Lincoln could lead to increased hospitalizations, straining local healthcare resources and potentially impacting access to care for other patients. The disease’s severity and potential for mortality underscore the importance of prompt diagnosis, treatment, and preventive measures.
Economic Implications, Lincoln nh legionnaires disease
Outbreaks of Legionnaires’ disease can significantly impact Lincoln’s economy, particularly its tourism and hospitality industry. The potential for negative publicity surrounding outbreaks can deter visitors, leading to decreased revenue for hotels, restaurants, and other businesses. The economic impact could also extend to local residents, potentially affecting employment opportunities and the overall economic well-being of the community.
Impact on Tourism and Hospitality
Lincoln, NH, is known for its scenic beauty and outdoor recreation opportunities, attracting a large number of tourists each year. Outbreaks of Legionnaires’ disease could significantly impact the tourism industry by discouraging visitors due to concerns about their health and safety. This could lead to decreased bookings at hotels, restaurants, and other tourism-related businesses, resulting in economic losses for the community.
Community Response
The Lincoln community has a history of responding effectively to Legionnaires’ disease outbreaks. Following past outbreaks, the community has implemented proactive measures, including public health campaigns to raise awareness about the disease, its transmission, and preventive measures. These campaigns have focused on educating residents and visitors about the importance of maintaining water systems and practicing good hygiene.
Public Health Initiatives and Awareness Campaigns
The Lincoln community, in collaboration with local health officials, has implemented various public health initiatives and awareness campaigns related to Legionnaires’ disease. These initiatives include:
- Regular testing of water systems in public buildings and facilities.
- Educational programs for building managers and owners on water safety and Legionnaires’ disease prevention.
- Public awareness campaigns through local media and community events to educate residents and visitors about the disease, its symptoms, and prevention strategies.
These initiatives demonstrate the community’s commitment to safeguarding public health and mitigating the potential impact of Legionnaires’ disease outbreaks.
Prevention and Mitigation Strategies: Lincoln Nh Legionnaires Disease
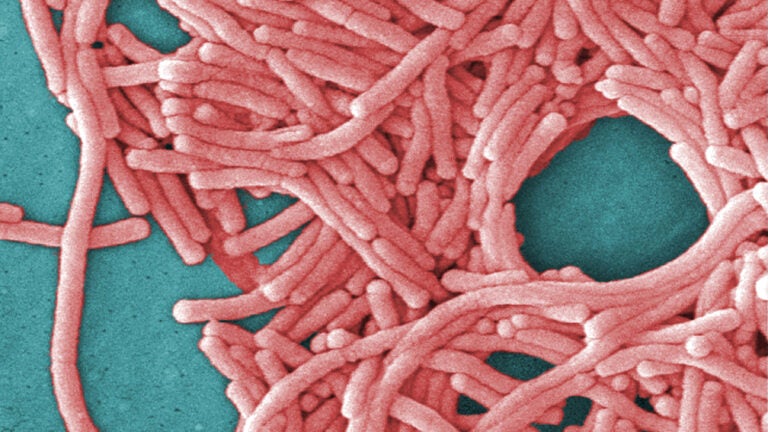
Preventing and mitigating Legionnaires’ disease in Lincoln, NH, is crucial to safeguarding public health. This involves understanding the disease’s transmission, implementing effective preventive measures, and taking proactive steps to minimize the risk of outbreaks.
Water Management Practices
Proper water management is essential for preventing Legionnaires’ disease. This includes:
- Maintaining Water Temperature: Keeping hot water temperatures above 120°F and cold water temperatures below 60°F can inhibit the growth of Legionella bacteria.
- Regular Flushing: Regularly flushing water systems, especially those that are infrequently used, helps prevent stagnant water where Legionella can thrive.
- Monitoring Water Quality: Testing water samples for the presence of Legionella bacteria is crucial, especially in high-risk facilities such as hospitals and hotels.
Building Maintenance
Maintaining buildings and their water systems is vital for preventing Legionnaires’ disease. This involves:
- Regular Cleaning and Disinfection: Cleaning and disinfecting water tanks, pipes, and other water-related fixtures can eliminate Legionella bacteria.
- Addressing Leaks and Corrosion: Promptly repairing leaks and addressing corrosion in water systems can prevent the creation of environments conducive to Legionella growth.
- Maintaining Cooling Towers: Regularly inspecting and maintaining cooling towers, which are known sources of Legionella, is essential for preventing outbreaks.
Individual Hygiene
Individual hygiene practices play a role in minimizing the risk of Legionnaires’ disease. This includes:
- Showering Regularly: Showering regularly can help wash away any Legionella bacteria that may have come into contact with the skin.
- Avoiding Inhalation of Mist or Aerosols: Avoiding exposure to mist or aerosols from water sources, such as hot tubs or fountains, can reduce the risk of inhaling Legionella bacteria.
Mitigation Strategies for Outbreaks
When Legionnaires’ disease outbreaks occur, prompt and effective mitigation strategies are essential. This involves:
- Identifying the Source: Identifying the source of the outbreak is crucial for taking targeted preventive measures.
- Treating Infected Individuals: Prompt medical treatment for infected individuals is essential for reducing morbidity and mortality.
- Public Health Interventions: Public health interventions, such as issuing health advisories and providing information about the outbreak, can help prevent further spread.
Effectiveness of Prevention and Mitigation Strategies
The effectiveness of different prevention and mitigation strategies has been studied extensively. For example, a study published in the journal “Emerging Infectious Diseases” found that regular water management practices, including flushing and temperature control, significantly reduced the risk of Legionnaires’ disease outbreaks in healthcare facilities. Similarly, studies have shown that prompt treatment with antibiotics can improve outcomes for infected individuals.
Recommendations for Improving Prevention Efforts in Lincoln, NH
To further enhance Legionnaires’ disease prevention efforts in Lincoln, NH, the following recommendations are crucial:
- Increase Public Awareness: Raising public awareness about Legionnaires’ disease, its symptoms, and prevention strategies is essential.
- Strengthen Water Management Regulations: Implementing stricter water management regulations for public and private buildings can help minimize the risk of outbreaks.
- Enhance Surveillance and Reporting: Improving surveillance and reporting systems for Legionnaires’ disease can help identify outbreaks early and facilitate prompt intervention.
- Promote Collaboration: Encouraging collaboration between public health officials, healthcare providers, and building managers can facilitate effective prevention and mitigation efforts.
Lincoln nh legionnaires disease – The Lincoln, New Hampshire, Legionnaires’ disease outbreak serves as a stark reminder of the vulnerability of public health systems, especially when confronted with unforeseen challenges. The recent northeast Ohio emergency , while geographically distant, offers valuable lessons in disaster preparedness and resource allocation, highlighting the importance of proactive measures in mitigating the impact of such events.
The Lincoln outbreak underscores the need for robust public health infrastructure, capable of swiftly responding to and containing outbreaks, ensuring the safety and well-being of communities.
The Lincoln, New Hampshire Legionnaires’ disease outbreak was a stark reminder of the vulnerability of even the most seemingly secure environments. The disease, caused by a bacterium found in water sources, spread through the town like a whisper on the wind, leaving behind a trail of fear and uncertainty.
The invisible enemy, much like the simmering tensions between Iran and Israel, a history of escalating conflict and mistrust , can strike without warning, leaving communities grappling with the aftermath. The Lincoln outbreak, like the volatile geopolitical landscape, serves as a sobering reminder of the fragility of our world, where unseen threats can emerge from the most unexpected corners.
